Platform Guide
gVisor requires a platform to implement interception of syscalls, basic context
switching, and memory mapping functionality. Internally, gVisor uses an
abstraction sensibly called Platform. A simplified version of this
interface looks like:
type Platform interface {
NewAddressSpace() (AddressSpace, error)
NewContext() Context
}
type Context interface {
Switch(as AddressSpace, ac arch.Context) (..., error)
}
type AddressSpace interface {
MapFile(addr hostarch.Addr, f File, fr FileRange, at hostarch.AccessType, ...) error
Unmap(addr hostarch.Addr, length uint64)
}
There are a number of different ways to implement this interface that come with various trade-offs, generally around performance and hardware requirements.
Implementations
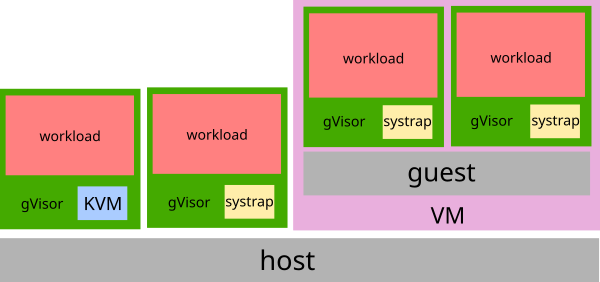
The choice of platform depends on the context in which runsc is executing. In
general, when running on bare-metal (not inside a VM), the KVM platform will
provide the best performance. The systrap platform is a better choice when
running inside a VM, or on a machine without virtualization support.
KVM
The KVM platform uses the kernel’s KVM functionality to allow the Sentry to act as both guest OS and VMM. The KVM platform runs best on bare-metal setups. While there is no virtualized hardware layer – the sandbox retains a process model – gVisor leverages virtualization extensions available on modern processors in order to improve isolation and performance of address space switches.
Note that while running within a nested VM is feasible with the KVM platform,
the systrap platform will often provide better performance in such a setup,
due to the overhead of nested virtualization.
systrap
The systrap platform relies seccomp’s SECCOMP_RET_TRAP feature in order to
intercept system calls. This makes the kernel send SIGSYS to the triggering
thread, which hands over control to gVisor to handle the system call. For more
details, please see
the systrap README file.
systrap replaced ptrace as the default gVisor platform in mid-2023. If you
depend on ptrace, and systrap doesn’t fulfill your needs, please
voice your feedback.
ptrace
The ptrace platform uses PTRACE_SYSEMU to execute user code without
allowing it to execute host system calls. This platform can run anywhere that
ptrace works (even VMs without nested virtualization), which is ubiquitous.
Unfortunately, the ptrace platform has high context switch overhead, so system
call-heavy applications may pay a performance penalty. For
this reason, systrap is almost always the better choice.
systrap replaced ptrace as the default gVisor platform in mid-2023. While
ptrace continues to exist in the codebase, it is no longer supported and is
expected to eventually be removed entirely. If you depend on ptrace, and
systrap doesn’t fulfill your needs, please
voice your feedback.
Changing Platforms
See Changing Platforms.